能動フィルタのインピーダンスを求めます。
具体例として以下の回路を考えます。
回路図エディタとして、回路シミュレータのPSIMを利用しました。PSIMは素子数と機能が限定されたデモ版がフリーで使うことができます。
PSIMから上記回路のネットリストをファイル名active_filter.cctで保存します。
.TIME 1E-005 0.01 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 R R1 1 2 8k 0 R R2 3 4 500 0 R R3 1 5 50 0 C C1 4 2 0.1u 0 0 C C2 4 1 0.1u 0 0 OP_AMP U1 0 2 1 5 -5 C C3 5 6 1000p 0 0 OP_AMP U2 6 7 7 5 -5 C C4 5 7 0.01u 0 0 R R4 6 0 1k 0 VP V2 7 VSIN V1 3 0 220 50 0 0 0
このようなネットリストから、回路が満たすべき制約条件(電流保存、オームの法則などなど)を方程式として出力する解析パッケージを作成しましょう。
/* * circuits.mac * electric circuit analysis package * author: ICHIKAWA, Yuji * date: 2011/06/07 * Copyright (C) 2011 ICHIKAWA, Yuji */ kirchhoff_laws(I, net) ::= buildq([I, net], block([result : [], net_without_gnd], net_without_gnd : rest(net, 1), for e in net_without_gnd do ( result : endcons(lsum(I[i], i, e) = 0, result)), return(result)))$ parts_laws(V, I, parts, net) ::= buildq([V, I, parts, net], block([result : [V[1] = 0]], /* Ground voltage = 0 */ for e in parts do ( if e[kind_index] = VP then /* Probes should have infinite impedance. */ result : endcons(I[e[terminal_index][1]] = 0, result) elseif member(e[kind_index], two_terminal_parts) then block([nodes, Z], result : endcons(lsum(I[i], i, e[terminal_index]) = 0, result), nodes : terminals_to_nodes(e[terminal_index], net), if e[kind_index] = VSIN then result : endcons(V[nodes[1]] - V[nodes[2]] = 1, result) else ( Z : if e[kind_index] = R then e[symbol_index] elseif e[kind_index] = C then 1/(%i*omega*e[symbol_index]) elseif e[kind_index] = L then %i*omega*e[symbol_index], result : endcons(V[nodes[1]] - V[nodes[2]] = Z*I[e[terminal_index][1]], result))) elseif e[kind_index] = OP_AMP then block([nodes], result : append(result, [I[e[terminal_index][1]] = 0, I[e[terminal_index][2]] = 0]), nodes : terminals_to_nodes(e[terminal_index], net), result : endcons(V[nodes[1]] = V[nodes[2]], result))), return(result)))$ load_netlist(file) := block([fs, parts : [], n, nodes, line, terminal : 0], fs : openr(file), n : length(node_list(fs)), close(fs), nodes : makelist([], i, 1, n), fs : openr(file), while (line : readline(fs)) # false do block([pl], pl : parse_line(line), if pl # [] then block([terminals : []], for i in pl[terminal_index] do ( terminal : terminal + 1, nodes[i + 1] : endcons(terminal, nodes[i + 1]), terminals : endcons(terminal, terminals) ), pl[terminal_index] : terminals, parts : endcons(pl, parts))), close(fs), return([terminal, parts, nodes]))$ /* functions for internal use */ /* PSIM netlist (.cct) constants */ node_index : 3 $ /* parts list constants */ terminal_index : 3 $ /* common parts list constants */ symbol_index : 2 $ kind_index : 1 $ two_terminal_parts : [R, C, L, VSIN]$ three_terminal_parts : [OP_AMP]$ one_terminal_parts : [VP]$ number_of_terminals(kind) := if member(kind, two_terminal_parts) then 2 elseif member(kind, three_terminal_parts) then 3 elseif member(kind, one_terminal_parts) then 1 else error("unknown part")$ value_index(kind) := node_index + number_of_terminals(kind)$ /* example: [R, R1, [0, 1], [1e3]] */ parse_line(str) := block([ts, result : [], value_i], ts : tokens(str), if charat(ts[kind_index], 1) = "." then return([]), for i : 1 thru symbol_index do result : endcons(parse_string(ts[i]), result), value_i : value_index(result[kind_index]), result : endcons(makelist(parse_string(ts[i]), i, node_index, value_i - 1), result), result : endcons(makelist(prefix_to_number(ts[i]), i, value_i, length(ts)), result), return(result))$ /* transform prefix of unit to number */ prefix_to_number(str) := block([last_char : charat(str,slength(str))], if digitcharp(last_char) then parse_string(str) else parse_string(substring(str, 1, slength(str))) * assoc(last_char, ["k"=1e3, "m"=1e-3, "u"=1e-6, "n"=1e-9, "p"=1e-12], 1))$ node_list(file_stream) := block([nodes : {}, line], while (line : readline(file_stream)) # false do block([ts], ts : parse_line(line), if ts # [] then nodes : union(setify(ts[node_index]), nodes)), return (listify(nodes)))$ terminals_to_nodes(terminals, net) := block([result : []], for e in terminals do ( for i : 1 thru length(net) do ( if member(e, net[i]) then (result : endcons(i, result), return()))), return(result))$
使用した機能
- buildq
- openr
- close
- readline
- charat
- digitcharp
- parse_string
- substring
- slength
- {}
- union
- setify
- listify
load_netlistは、PSIMのネットリストファイルを読み込み、通しの端子番号を生成して、総端子数と解析用の部品リスト、ネットリストを返します。
kirchhoff_lawsは、Kirchhoffの法則に基づく方程式をネットリストから生成します。
parts_lawsは、Ohmの法則などに基づく部品が満たすべき方程式を部品リスト、ネットリストから生成します。
では、具体例を解かしてみましょう。
/* 8.1.9m */ load("circuits")$ [t, parts, net] : load_netlist("active_filter.cct"); eqns : append(kirchhoff_laws(I, net), parts_laws(V, I, parts, net)); sol : solve(eqns, append(makelist(V[i], i, 1, length(net)), makelist(I[i], i, 1, t)))$ V[8], sol;
わかりにくいので、具体的な回路パラメータを入れてみましょう。
/* 8.1.10m */ v8s : ratsimp(V[8]), solutions, R1 = 8000, R2 = 500, R3 = 50, R4 = 1000, C1 = 10^(-7), C2 = 10^(-7), C3 = 10^(-9), C4 = 10^(-8);
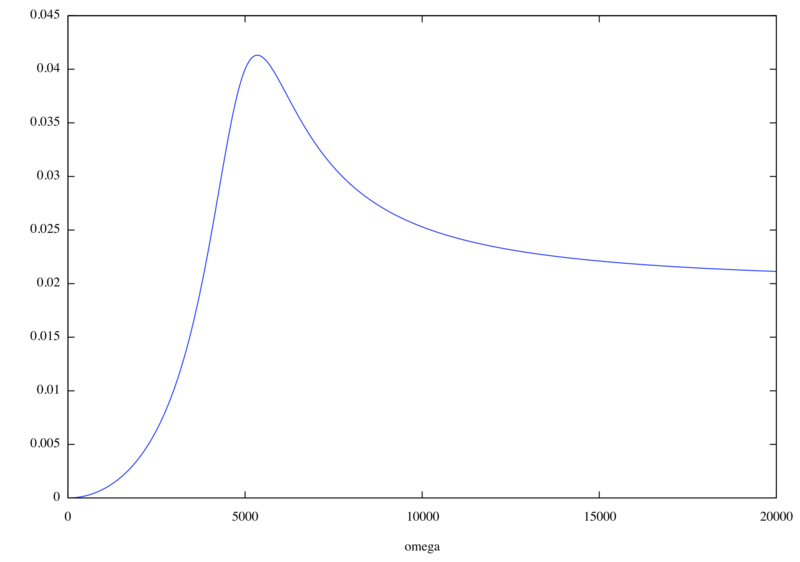
このゲインをプロットしてみましょう。
plot2d(cabs(v8s), [omega, 0, 20000]);
参考文献
- Crandall, Mathematica―理工系ツールとしての (アジソン ウェスレイ・トッパン情報科学シリーズ) p.229-p.234
使用ツール
- Powersim社, 回路シミュレータPSIM